Note 9: Hashing
Author: Zhen Tong 120090694@link.cuhk.edu.cn Lecturer: Jane YOU
Hash
Hash
Motivation: Using Hash to decrease searching complexity to
bucket: contains one or more entries
We use the hash function to get the bucket of a search key
Because different search keys should be mapped to the same bucket, we need to do searching in one bucket.
hash index: bucket contains entries with pointer linked to record
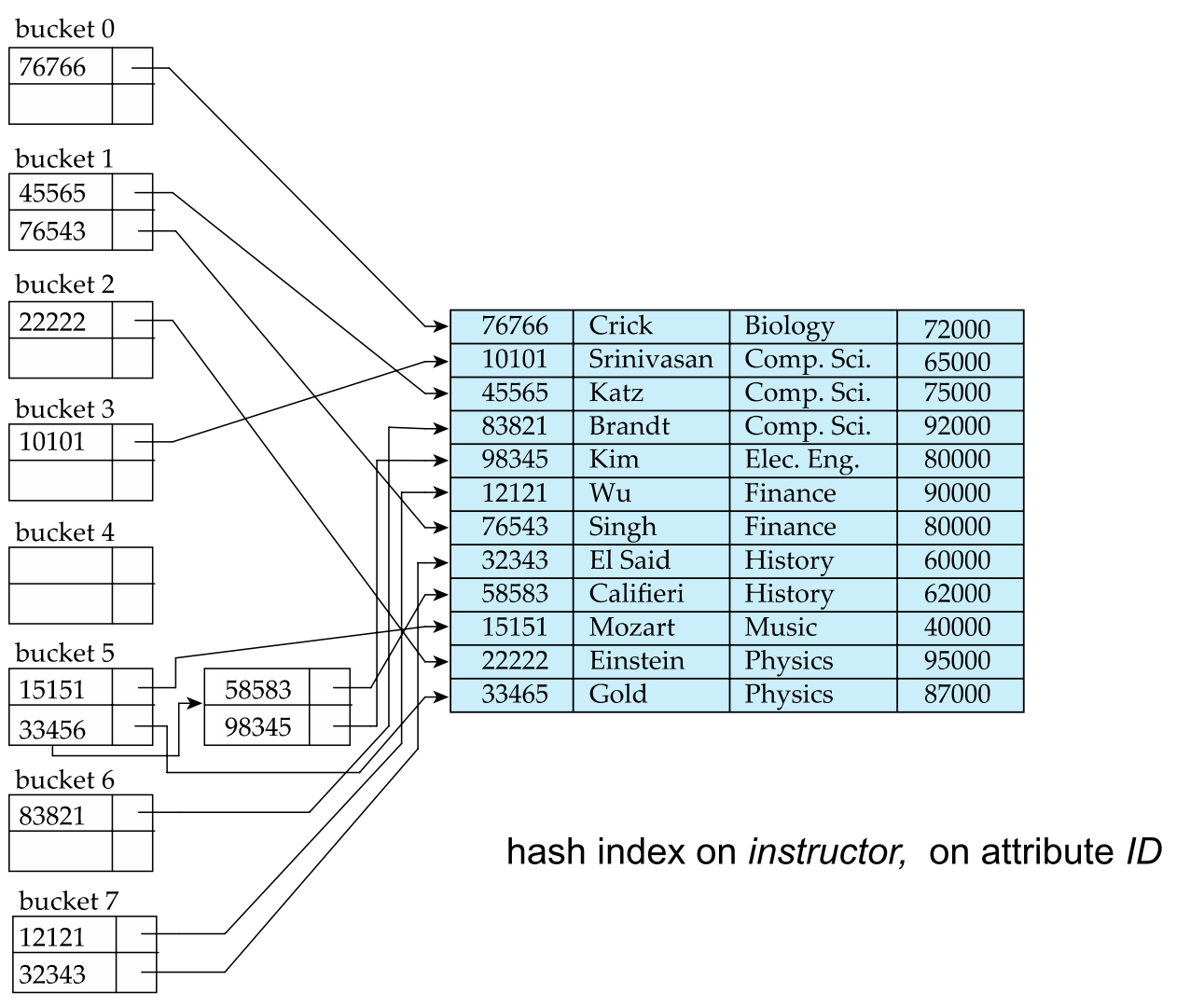
hash file-organization: hash file-organization
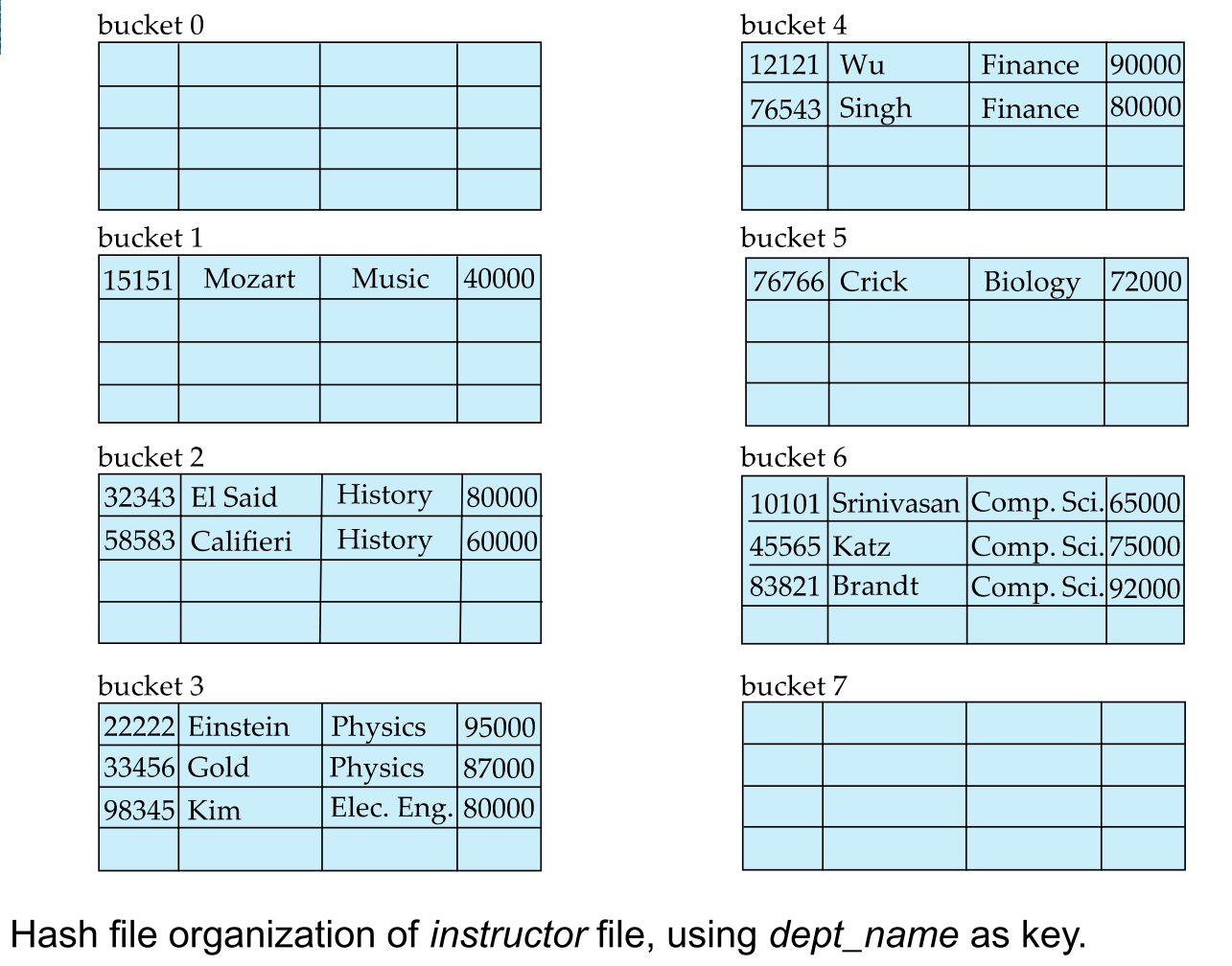
uniform is good
We try to avoid collision. Each bucket assigns the same number of search key values to the entries in the target storage. An ideal hash function is random. Therefore, what ever the distribution of the search key follows, the bucket can have same numbers of record
- For example, for a string search key, you can add the binary representation of all characters in the string and return a sum modulo to the number of buckets
Hash Bucket Overflow
Bucket overflow:
- There is limited space in one bucket
- The record buckets is skew can be caused by:
- Multiple records have the same search key value
- The selected hash function produces a non-uniform distribution of key values
If we have records and numbers of buckets with a capacity of , then the probability for each record throw to each bucket is . Assum the number of records in one bucket is a random variable called . Then for one specific bucket, the probability of overflow is
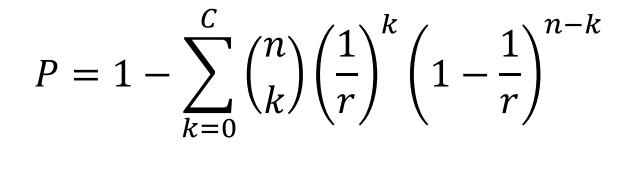
Overflow Policy
Collision: Insert the hash field value of the record hash to an address that is already occupied
Collision Resolution
Open Addressing: Start with the occupied location, find the next unused location, and place the record there
Overflow Chain: The overflow buckets of a given bucket are linked in a linked list
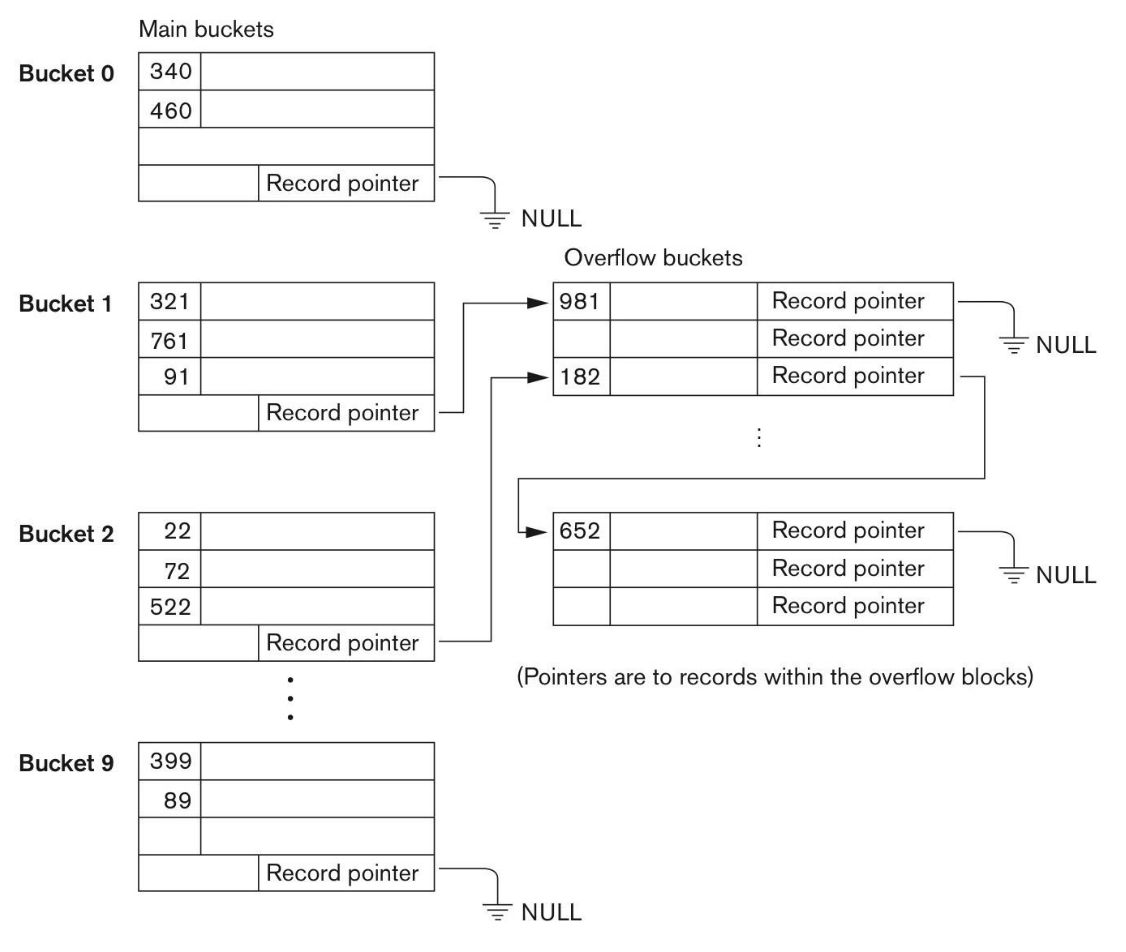
Overflow Chain Disadvantages of static hashing:
In a static hash, the function maps the search key value to a fixed set of bucket addresses, but the database grows or shrinks over time
- If the initial number of buckets is too small, excessive overflows can cause performance degradation when files grow
- If you allocate space for expected growth, a lot of space will be wasted (the bucket will be filled) in the beginning.
- If the database shrinks, the space is wasted again
Hashing with Dynamic File Expansion
The result of a hash function is a non-negative integer, so it can be expressed as a binary number
hash value of the record
The rule of visiting one bucket is built on the binary representation of the result of the hash function, which is a string of bits called a record hash
records is assigned to certain buckets by the fist few bits of the hash value
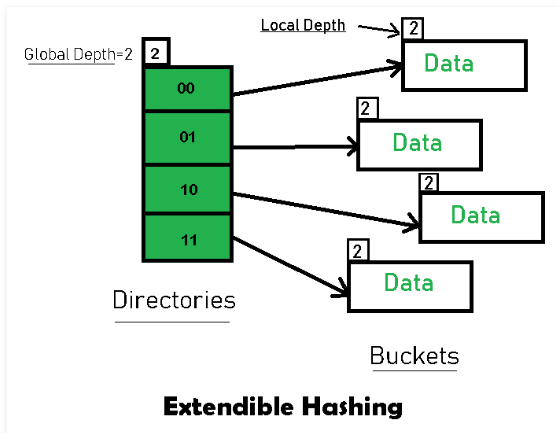
extendible hashing
Introduction
Motivation: Construct a bucket array of length
The first bit of the hash value is used as the index of the array to determine the directory entry, and the address in the entry determines which bucket the corresponding record is stored in
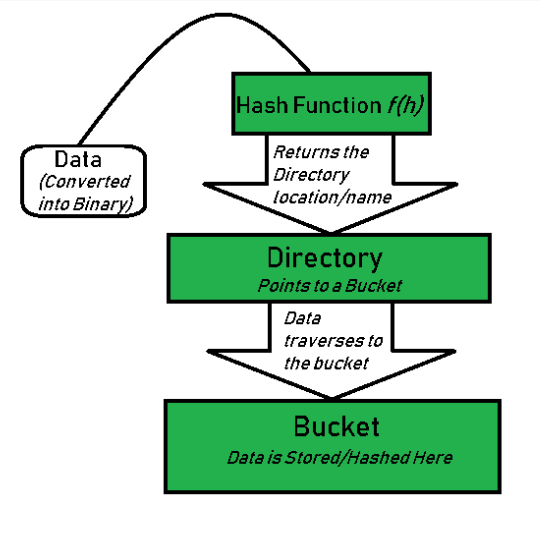
extendible hashing is a dynamic hashing method where directory and bucket are used to hash data. This is a very flexible approach, in which the hash function also undergoes dynamic changes
The main features of extensible hashing are:
- directory :directory stores the address of the bucket in the pointer. Assign an id to each directory, which may change when directory expansion occurs
- Global Depth = Number of bits in directory id. Global Depth = Number of bits in directory id. They represent the number of bits used by the hash function to classify the key. Global Depth:与Directories相关联. Global Depth = Number of bits in directory id. 它们表示哈希函数用于对键进行分类的bit数。
- Local Depth: Associated with buckets, the local depth is always less than or equal to the global depth. The local depth determines the action to be performed in the event of an overflow based on the global depth Local Depth: 与buckets相关联,局部深度总是小于或等于全局深度。局部深度根据全局深度来决定在发生溢流时要执行的动作
- Bucket Splitting: When the number of elements in a Bucket exceeds a specific size, the Bucket is split into two parts. Bucket Splitting: 当Bucket中的元素数量超过特定的大小时,则将Bucket分成两部分。
- Directory Expansion: Directory expansion when buckets overflow. When the local depth of the overflow bucket is equal to the global depth, expand the directory Directory Expansion: 当桶溢出时进行目录扩展。当已溢出桶的局部深度等于全局深度时,执行目录扩展
Basic Working of Extendible Hashing:
- Step 1, analyze the data elements: Data elements may exist in various forms. Integer, string, floating point number, etc. For now, let's consider data elements of type integer. For example :49.
- Step 2, convert to binary format:
Converts data elements to binary format. For string elements, consider the ASCII equivalent integer of the starting character, and then convert that integer to binary form. Since we have 49 as the data element, its binary form is 110001.
- Step 3 - View the Global Depth of the directory. Assume that the global depth of the hash directory is 3.
- Step 4 - Identify the directory: Consider the number of "global depths" of the LSB in the binary and match it to the directory id. For example. The resulting binary number is 110001 and the global-depth is 3. Therefore, the hash function will return (110001, which is 001).
- Step 5 - Navigation: Now navigate to the bucket pointed to by directory 001.
- Step 6 - Insert and Overflow check: Insert components and check whether the bucket overflows. If yes, go to Step 7; otherwise, go to Step 9.
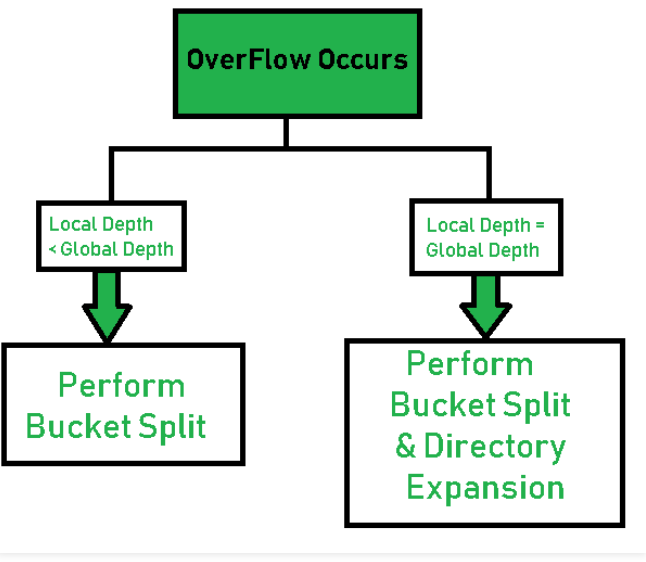
- Step 7 - Handle Over Flow Condition during Data insert : a Bucket overflow can occur when inserting a Bucket. In such cases, we need to follow proper procedures to avoid incorrect handling of the data.
First, check whether the local depth is less than or equal to the global depth. Then choose one of the following examples.
Case1:If the local depth of the overflow bucket is equal to the global depth, run directory expand and bucket split. The global depth and local depth values are then increased by 1 each. Then, assign the appropriate pointer. The directory extension doubles the number of directories in the hash structure.
Case2:If the local depth is less than the global depth, only Bucket Split is performed. Then only increase the local depth value by 1. Then, assign the appropriate pointer.
- Re-hashing of split bucket elements: The elements present in the split overflow bucket will be re-hashed at the new global depth of the directory.
- Done
Example
Hash these elements:16、4、6、22、24、10、31、7、9、20、26。
Bucket Size:3 (Assume)
Hash Function:
Suppose the global depth is X. Then the Hash Function returns X LSBs.
binary forms
16- 10000
4- 00100
6- 00110
22- 10110
24- 11000
10- 01010
31- 11111
7- 00111
9- 01001
20- 10100
26- 11010
Extendible Hashing (Dynamic approach to DBMS) - GeeksforGeeksExtendible Hashing is a dynamic hashing method wherein directories, and buckets are used to hash data. It is an aggressively flexible method in which the hash function also experiences dynamic changes. Main features of Extendible Hashing: The main features in this hashing technique are: Directories: The directories store addresses of the buckets in pointers. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/extendible-hashing-dynamic-approach-to-dbms/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/extendible-hashing-dynamic-approach-to-dbms/